Here we will learn about constructing triangles, including how to accurately draw different triangles using a pencil, a ruler, a protractor and a pair of compasses.
There are also constructions worksheets, including constructing triangles, based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
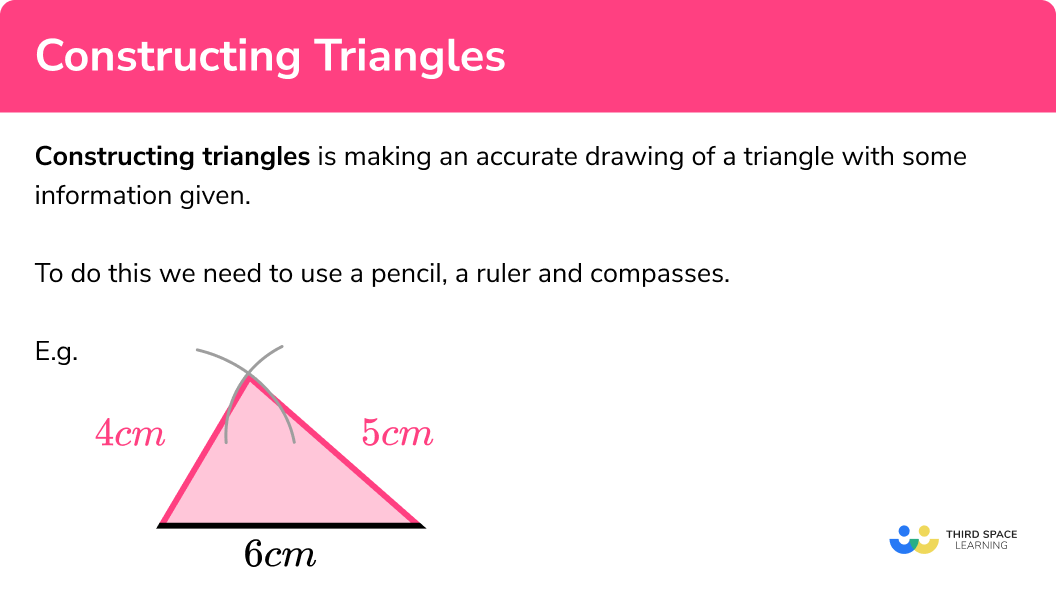
Constructing triangles is making an accurate drawing of a triangle with some information given.
To do this we need to use a pencil, a ruler and compasses.
Here is a triangle with sides 4cm , 5cm and 6cm constructed using a pencil, a ruler and compasses.

In order to accurately construct a triangle given all three sides (SSS):


Get your free constructing triangles worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.


Get your free constructing triangles worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
Constructing triangles is part of our series of lessons to support revision on construction and loci and construction. You may find it helpful to start with the main loci and construction lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
Draw the triangle ABC accurately
Use a pencil and a ruler to draw the base. It is usually easiest to use the longest side.
2 Set compasses for the second side and draw an arc.
Open the compasses to 4cm . Place the point on point A and draw an arc.
3 Set compasses for the third side and draw an arc.
Open the compasses to 6cm . Place the point on point C and draw an arc. This second arc should cross the first arc.
4 Join up the intersection of the arcs.
Complete the triangle by joining the point where the arcs intersect to point A and point C .
Draw the triangle RST accurately
Draw the base.
Use a pencil and a ruler to draw the base. It is usually easiest to use the longest side.
Set compasses for the second side and draw an arc.
Open the compasses to 4.6cm . Place the point on point R and draw an arc.
Set compasses for the third side and draw an arc.
Open the compasses to 6.2cm . Place the point on point T and draw an arc. This second arc should cross the first arc.
Join up the intersection of the arcs.
Complete the triangle by joining the point where the arcs intersect to point R and point T .
In order to accurately construct a triangle given two angles and the included side (ASA):
 the included side" width="1056" height="599" />
the included side" width="1056" height="599" />
Draw the triangle ABC accurately
Draw the base.
Use a pencil and a ruler to draw the base.
At one end point measure one angle.
At point A use a protractor to measure the angle 50° , make a mark and then draw a straight line from point A through the mark. Make this line long.
At the other end point measure the second angle.
At point B use a protractor to measure the angle 30° , make a mark and then draw a straight line from point B though the mark.
Complete the triangle.
Make sure that the two lines interact to form the triangle.
Draw the triangle ABC accurately
Draw the base.
Use a pencil and a ruler to draw the base.
At one end point measure one angle.
At point A use a protractor to measure the angle 25° , make a mark and then draw a straight line from point A through the mark. Make this line long.
At the other end point measure the second angle.
At point B use a protractor to measure the angle 63° , make a mark and then draw a straight line from point B though the mark.
Complete the triangle.
Make sure that the two lines interact to form the triangle.
In order to accurately construct a triangle given two sides and the included angle (SAS):
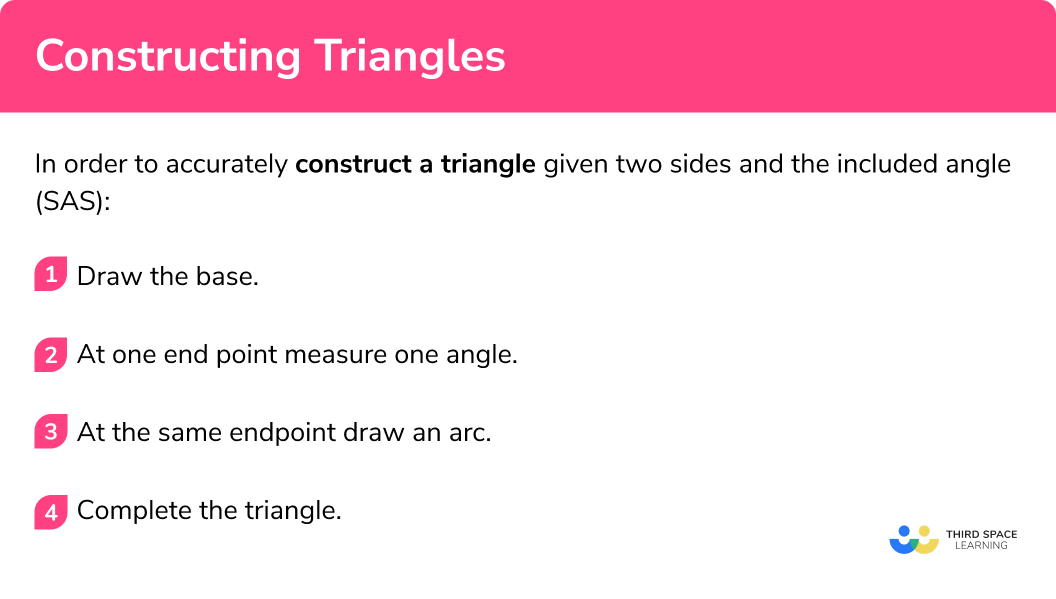
Draw the triangle ABC accurately
Draw the base.
Use a pencil and a ruler to draw the base.
At one end point measure one angle.
At point B use a protractor to measure the angle 40° , make a mark and then draw a straight line from point B through the mark. Make this line long.
At the same endpoint draw an arc.
Open the compasses to 5cm . Place the point on point B and draw an arc. This second arc should cross the line drawn in step 2.
Complete the triangle.
Join the intersection of the arc and the line with point A .
Draw the triangle DEF accurately:
Draw the base.
Use a pencil and a ruler to draw the base.
At one end point measure one angle.
At point E use a protractor to measure the angle 73° , make a mark and then draw a straight line from point E through the mark. Make this line long.
At the same endpoint draw an arc.
Open the compasses to 5.2cm . Place the point on point B and draw an arc. This second arc should cross the line drawn in step 2.
Complete the triangle.
Join the intersection of the arc and the line with point A .
A sharp pencil helps your diagram to be accurate. Using a small pencil in compasses can also be helpful.
The arcs drawn should be drawn lightly so can be adjusted if needed but they must be visible in your final answer. This is to show that you have used the correct method to draw the triangle accurately.
Remember to measure angles from 0 .
If you are given two angles and the side is not included you can work out the third angle by using the fact that the sum of interior angles in a triangle is 180° . Then you can use the two angles and included side detailed above.
1. Construct a triangle with sides 4cm , 5cm and 6cm .




The longest side should be 6cm . Compasses should be used to make the arcs, and they should be clearly seen. The other two sides are of different lengths; 4cm and 5cm .
2. Construct a triangle with sides 7cm , 6cm and 6cm .




The longest side should be 7cm . Compasses should be used to make the arcs, and they should be clearly seen. The other two sides are the same length; 6cm . The triangle is an isosceles triangle.
3. Construct a triangle ABC , with AB is 6cm , angle BAC is 45^ and angle ABC is 60^ .




Check the labelling of the triangle. The side AB should be 6cm . The angle at A should be 45^ and angle at B should be 60^ .
4. Construct a triangle PQR , with PQ is 7cm , angle QPR is 40^ and angle PQR is 45^ .




Check the labelling of the triangle. The side PQ should be 7cm . The angle at P should be 40^ and angle at Q should be 45^ .
5. Construct a triangle ABC , with AB is 6cm , BC is 5cm and angle ABC is 60^ .




Check the labelling of the triangle. The side AB should be 6cm and the side BC should be 7cm . The angle at B should be 60^ .
6. Construct a triangle ABC , with AB is 6cm , BC is 5cm and angle ABC is 60^ .




Check the labelling of the triangle. The side RS should be 7cm and the side ST should be 6cm . The angle at S should be 50^ .
1. In the space below, use a ruler and compasses to construct an equilateral triangle with sides 7cm .
You must show all your construction lines.
One side of the triangle has already been drawn for you.
(2 marks)
Show answer
for the construction arcs
(1)
for the completed equilateral triangle
(1)
2. Here is a triangle
Make an accurate drawing of the triangle ABC .
The line AB has already been drawn for you.
(2 marks)
Show answerfor the angle B 38-42 degrees OR for the side BC 6.3-6.7cm
(1)
for the completed triangle
(1)
3. Here is a triangle
Make an accurate drawing of the triangle ABC .
The line AB has already been drawn for you.
(2 marks)
Show answerfor the angle 68-72 degrees OR for the angle 48-52 degrees
(1)
for the completed triangle
(1)
You have now learned how to:
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.

© 2024 Third Space Learning. All rights reserved.
Third Space Learning is the trading name of Virtual Class Ltd
We use essential and non-essential cookies to improve the experience on our website. Please read our Cookies Policy for information on how we use cookies and how to manage or change your cookie settings.Accept
Privacy & Cookies PolicyThis website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Out of these, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. But opting out of some of these cookies may affect your browsing experience.
Always EnabledNecessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.
Non-necessaryAny cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies. It is mandatory to procure user consent prior to running these cookies on your website.